Package tsflex
flexible time-series operations
This is the documentation of tsflex; a sequence first Python toolkit for
processing & feature extraction, making few assumptions about input data.
This makes tsflex suitable for use-cases such as inference on streaming data, performing operations on irregularly sampled series, a holistic approach for operating on multivariate asynchronous data, and dealing with time-gaps.
~ With great flexibility comes great responsibility, read our docs! - the tsflex devs
Jump to API reference
Getting started 🚀
tsflex serves three main functionalities; series processing, feature extraction and chunking:
- The processing module withholds a
SeriesPipelinein which uni- and multivariate data processing operations can be defined. - The feature extraction module defines a
FeatureCollectionwhich mainly serves as a registry of defined features and allows performing highly-customizable strided-rolling feature extraction. - The chunking module withholds
chunk_data(); a method which returns continuous data-chunks, based on passed arguments such as min_chunk_dur. The user can then use these data-chunks for either processing or feature extraction.
Data formats 🗄️
tsflex leverages the flexibility and convenience that Pandas delivers. This has the consequence that your input should always be either one or more pd.Series/pd.DataFrame. Using type-hinting, the input-data can be defined as:
import pandas as pd; from typing import Union, List
data: Union[pd.Series, pd.DataFrame, List[Union[pd.Series, pd.DataFrame]]]
For brevity, we call an item from data, i.e., series or dataframe-column, a time-series (ts).
Wide vs. Long Data
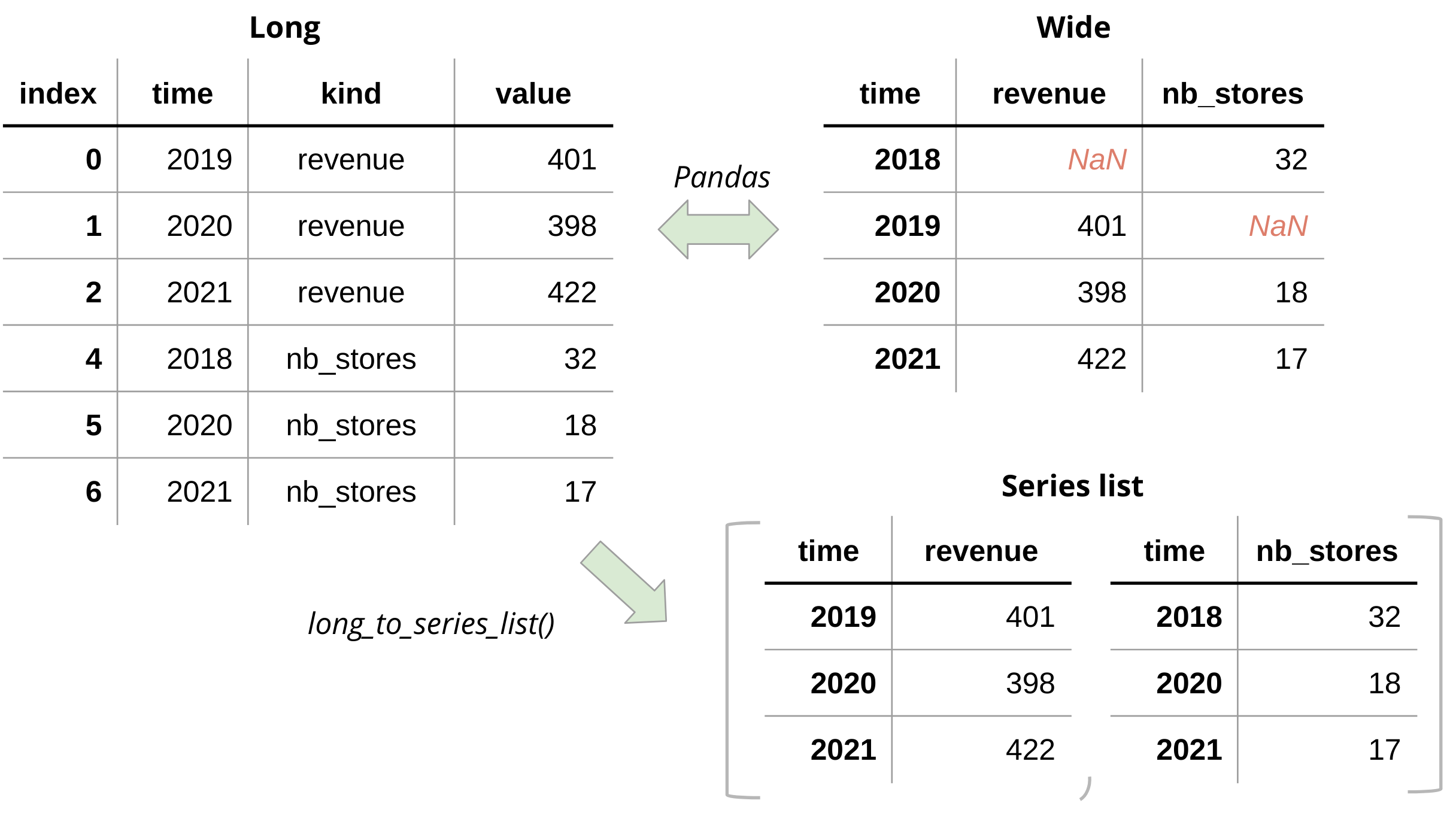
Time series data is often stored in 2 data-types:
Widetime-series data, also known as flat data, is the most common variant. Each column represents a data-modality and the index is the shared time.
Note: As shown in top-right table of the example above, not all data-modalities might have values for the shared (~union) index. This circumstance introduces Not a Number (NaN) entries.
It often makes more sense to treat such data as ats-list of which allNaNs are omitted (table right-bottom).Longtime-series data, which consists of 3 columns:- A non-index
time-column, which thus can withhold duplicates - A
kindcolumn, defining thetsits name. - A
valuecolumn, withholding the value for the corresponding kind-time combination
- A non-index
tsflex was built to support wide-dataframes & series-list data
Tip
If you use long data, you might want to convert this to other modalities.
As shown in the figure above, it is not recommended to transform long -> wide as this might introduce NaNs, potentially resulting in unwanted processing or feature-extraction behavior.
The snippet below provides the functionality for the long -> series-list transformation.
import pandas as pd; from typing import List
def long_dataframe_to_series_list(
long_df: pd.DataFrame, time_col: str, value_col: str, kind_col: str
) -> List[pd.Series]:
codes, uniques = pd.factorize(long_df[kind_col])
series_list = []
for idx, unique in enumerate(uniques):
series_list.append(
pd.Series(
data=long_df.loc[codes == idx, value_col].values,
index=long_df.loc[codes == idx, time_col],
name=unique,
)
)
return series_list
Supported data-types
tsflex
is rather versatile regarding the ts-data its types (e.g. np.float32, string-data, time-based data).
TODO: add examples of time-based / categorical / series-based function input features
Note: it is the end-users responsibility to use a function which interplays nicely with the data's format.
Comparison 🔎
The table below positions tsflex among other relative Python packages.
| tsflex v0.2.2 | seglearn v1.2.3 | tsfresh v.0.18.0 | TSFEL v0.1.4 |
Kats v0.1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||
| Sequence index requirements | Any - sortable | Any - is sorted |
Any - sortable | Any - is sorted | Datetime index |
| Multivariate time-series | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Unevenly sampled data | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Sequence column maintenance | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Retains output names | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Multiprocessing | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Operation Execution time logging | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Chunking (multiple) time-series | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Feature extraction | |||||
| Strided-window definition format | Sequence index range | Sample-based | Sample-based | Sample-based | Na. |
| Strided-window feature extraction | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Multiple stride-window combinations | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Custom Features | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| One-to-one functions | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| One-to-many functions | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Many-to-one functions | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Many-to-many functions | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Categorical data | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Input datatype preservation | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Benchmark 📊
The visualizations below compare tsflex v0.2.2 against other eligible packages for the strided-rolling feature extraction use-case.
As a reference, the data size when loaded in RAM was 96.4MB.
In the first figure, the shaded areas represent the lower an upper quantile range (q=[0.1, 0.9]) of the runs.
In the second figure, the performance of tsflex & other related packages is charted as times more efficient than tfresh (for both sequential and multiprocessing execution).
These figures are constructed by using the tsflex-benchmarking repo, we refer to this repository for more details.
Expand source code
"""<i><b>flex</b>ible <b>t</b>ime-<b>s</b>eries operations</i>
.. include:: ../docs/pdoc_include/root_documentation.md
.. include:: ../docs/pdoc_include/tsflex_matrix.md
"""
__docformat__ = "numpy"
__author__ = "Jonas Van Der Donckt, Jeroen Van Der Donckt, Emiel Deprost"
__version__ = "0.4.1"
__pdoc__ = {
# do not show tue utils module
"tsflex.utils": False,
# show the seriesprocessor & funcwrapper their call method
"SeriesProcessor.__call__": True,
"FuncWrapper.__call__": True,
}
__all__ = ["__version__", "__pdoc__"]API reference of tsflex
.chunking-
Utilities for chunking time-series data before feeding it to the operators.
.features-
Feature extraction submodule …
.processing-
Processing module …